8.1: Which One Doesn’t Belong: Histograms
Which histogram does not belong? Be prepared to explain your reasoning.
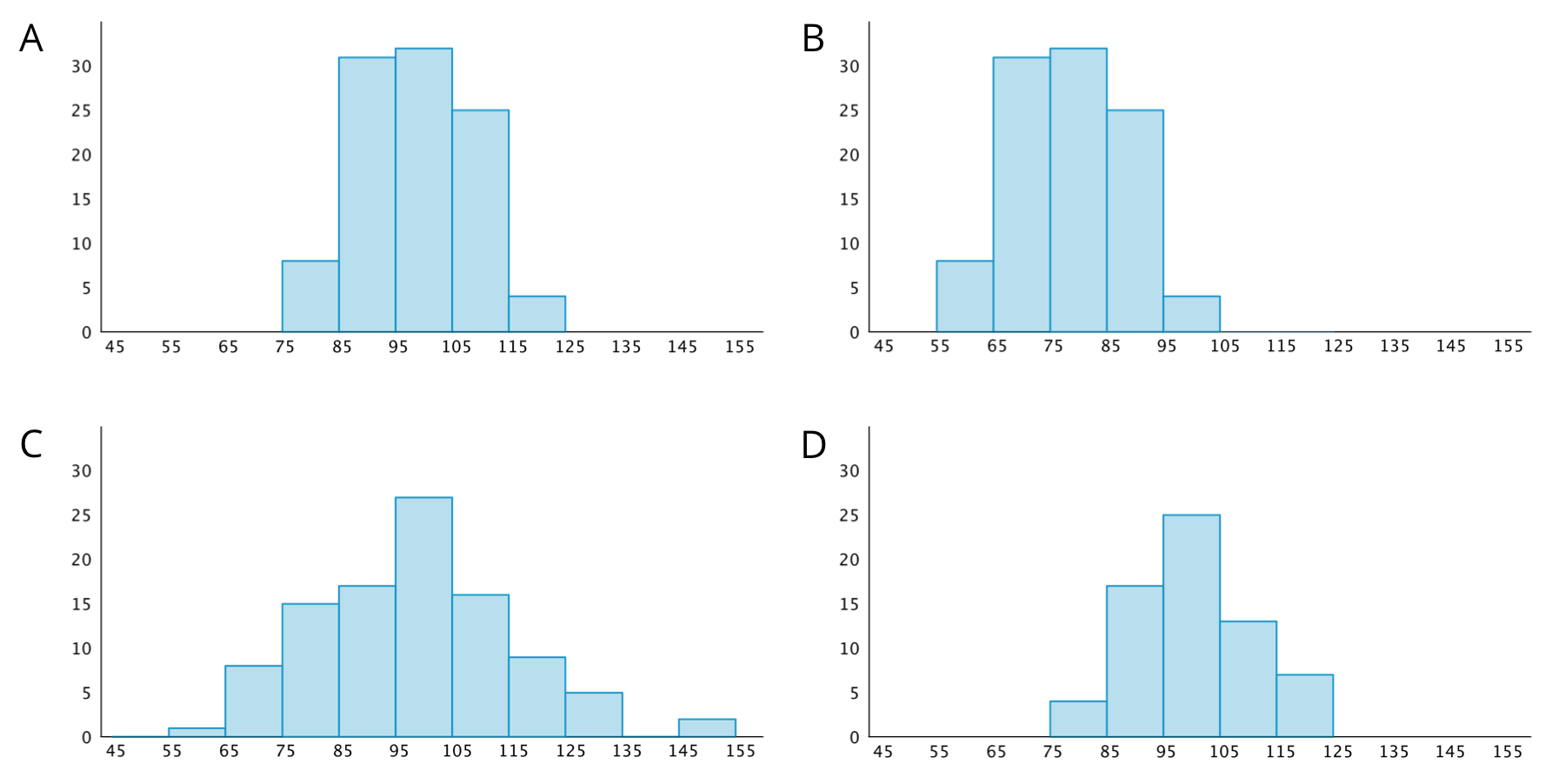
Let's describe distributions displayed in histograms.
Which histogram does not belong? Be prepared to explain your reasoning.

Discuss your sorting decisions with another group. Do both groups agree which cards should go in each pile? If not, discuss the reasons behind the differences and see if you can reach agreement. Record your final decisions.
Histograms that are approximately symmetrical:
Histograms that are not approximately symmetrical:
Histograms are also described by how many major peaks they have. Histogram A is an example of a distribution with a single peak that is not symmetrical.
Which other histograms have this feature?
Some histograms have a gap, a space between two bars where there are no data points. For example, if some students in a class have 7 or more siblings, but the rest of the students have 0, 1, or 2 siblings, the histogram for this data set would show gaps between the bars because no students have 3, 4, 5, or 6 siblings.
Which histograms do you think show one or more gaps?
Sometimes there are a few data points in a data set that are far from the center. Histogram A is an example of a distribution with this feature.
Would you describe any of the other histograms as having this feature? If so, which ones?
Your teacher will provide the data that your class collected on how students travel to school and their travel times.

Compare the histogram and the bar graph that you drew. Discuss your thinking with your partner:
Use one of these suggestions (or make up your own). Research data to create a histogram. Then, describe the distribution.
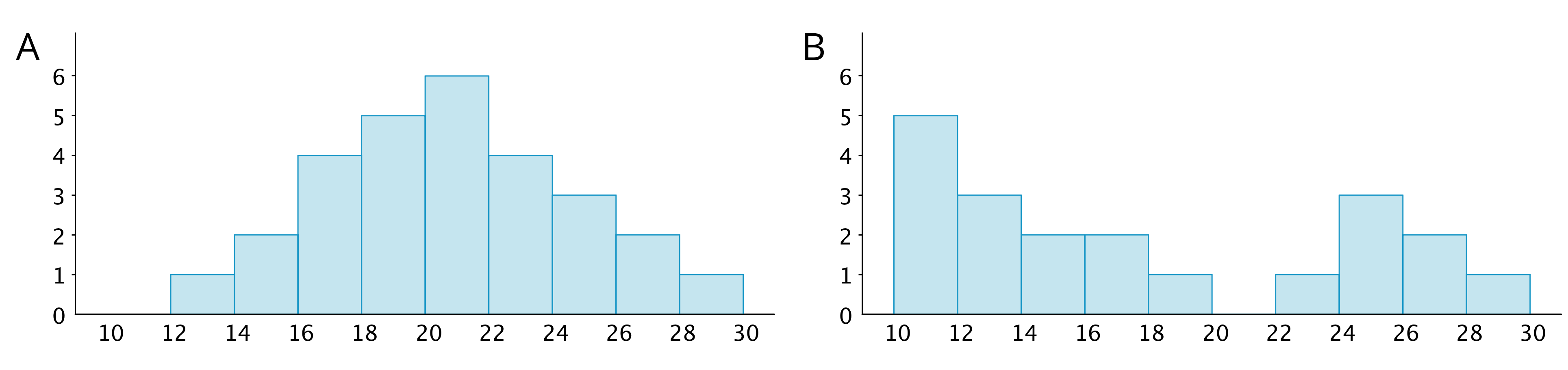
We can describe the shape and features of the distribution shown on a histogram. Here are two distributions with very different shapes and features.
Here is a bar graph showing the breeds of 30 dogs and a histogram for their weights.
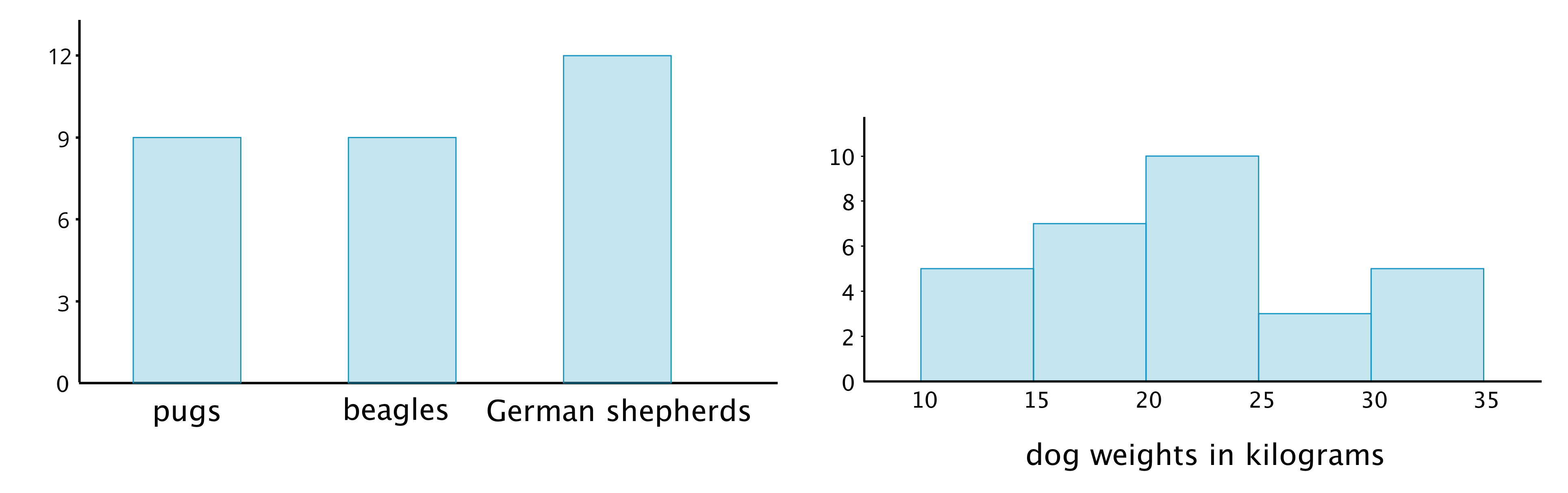
Bar graphs and histograms may seem alike, but they are very different.